What is ROAD DWI?
Change Data Propagation (CDP) Spotlight
Capture the deltas from sources without impacting the performance, then propagate the deltas into the warehouse.
Low latency
Stream changes within seconds with checkpointed, resumable pipelines.
Warehouse-native merges
Type-safe inserts & deletes via MERGE.

Exactly-once semantics
No duplicates, even on retries.

Propagate eligible changes
When slicing/subsetting the data only the eligible changes are propagated.
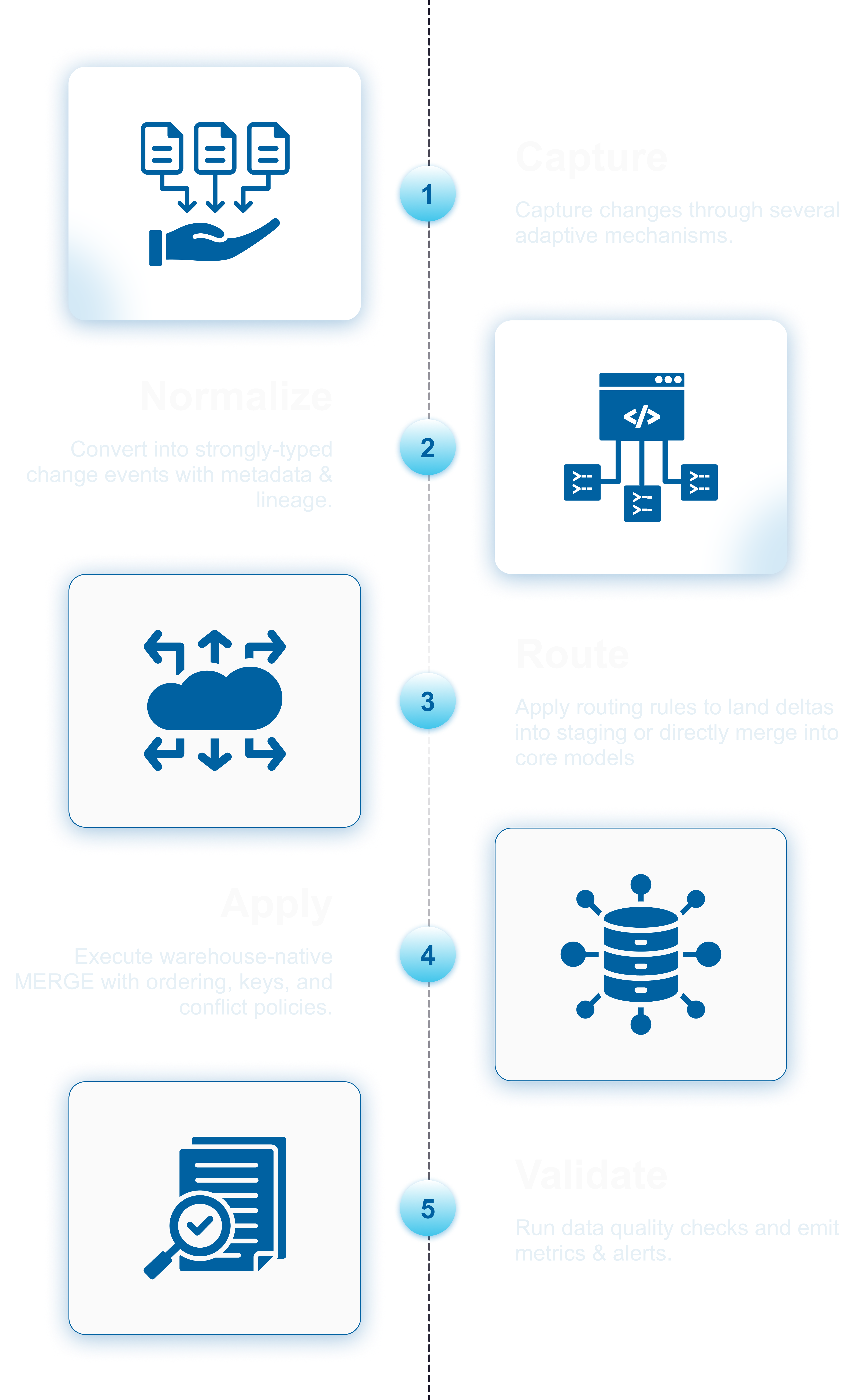
Capabilities

High-throughput batch
Parallel extract/load, file chunking, and avoid-merge strategy.
Schema evolution
Auto-migration, type mapping, and nullability guards during ingestion.
Governance & lineage
Data lineage, audits, PII/PCI/PHI masking, and encrypted data at-rest/in-flight.
Observability
SLIs, backpressure metrics, alerting, and replayable checkpoints.

Warehouse-native ELT
Push-down transforms for Snowflake, Postgres, and Oracle.

Extensible
Hooks for custom routing, Data Quality checks, and domain-specific transforms.
Data Transformations
Transform values via normalization, masking, encryption, and deduplication.